[Spring][Security] 스프링 시큐리티 재정리
들어가며
해당 게시글은 인프런 정수원 강사님의 스프링 시큐리티 - Spring Boot 기반으로 개발하는 Spring Security 강의를 바탕으로 쓰였음을 미리 밝힙니다.
스프링 시큐리티 기본 API 및 Filter 이해
사용자 정의 보안 기능 구현
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter상속- 인증 API
http.formLogin()
http.logout()
http.csrf()
http.httpBasic()
http.SessionManagement()
http.RememberMe()
http.ExceptionHandling ()
http.addFilter()
- 인가 API
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(/admin)
.hasRole(USER)
.permitAll()
.authenticated()
.fullyAuthentication()
.acess(hasRole(USER))
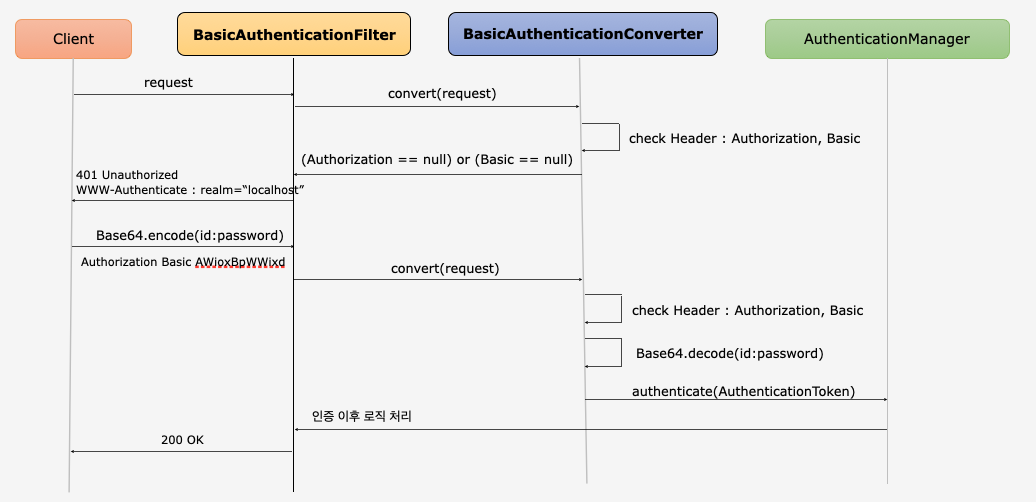
HTTP Basic 인증, BasicAuthenticationFilter
HTTP Basic 인증
- HTTP는 자체적인 인증 관련 기능을 제공하며 HTTP 표준에 정의된 가장 단순한 인증 기법이다
- 간단한 설정과 Stateless가 장점 - Session Cookie(JSESSIONID) 사용하지 않음
- 보호자원 접근시 서버가 클라이언트에게 401 Unauthorized 응답과 함께 WWW-Authenticate header를 기술해서 인증요구를 보냄
- Client는 ID:Password 값을 Base64로 Encoding한 문자열을 Authorization Header에 추가한 뒤 Server에게 Resource를 요청(Authorization: Basic cmVzdDpyZXN0)
- ID, Password가 Base64로 Encoding되어 있어 ID, Password가 외부에 쉽게 노출되는 구조이기 때문에 SSL이나 TLS는 필수이다
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.httpBasic();
}
BasicAuthenticationFilter
Form 인증
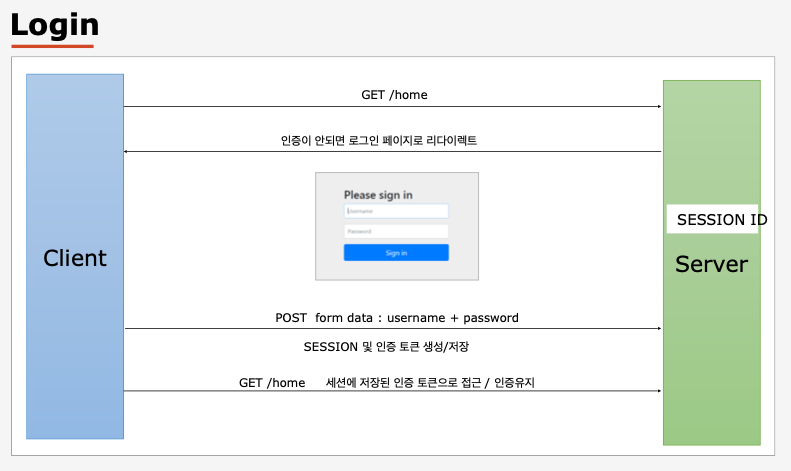
- 세션 아이디(JSESSIONID)를 키로 해서
SecurityContext를 세션 저장소에 저장
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html") // URI 설정도 가능
.defaultSuccessUrl("/home")
.failureUrl("/login.html?error=true")
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
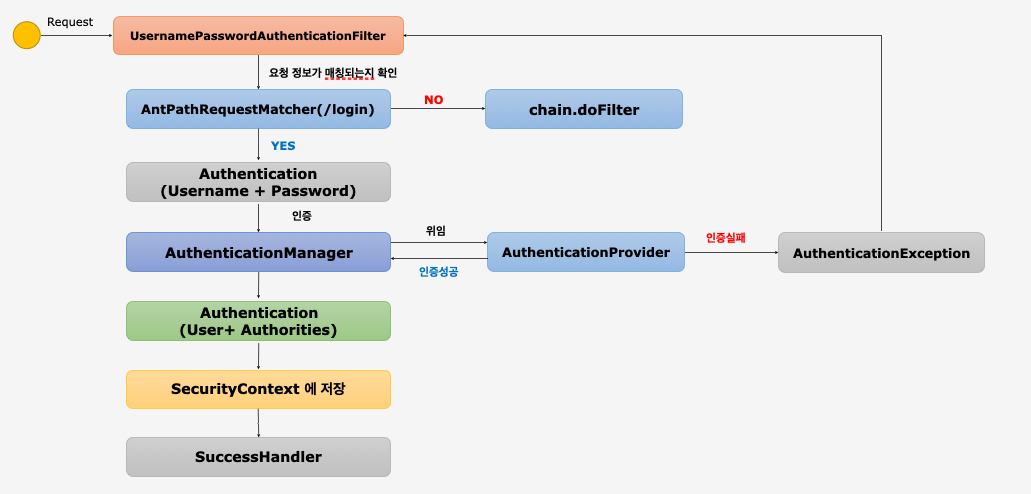
User는UserDetails구현체UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서 발생한AuthenticationException의 경우AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter에서 처리
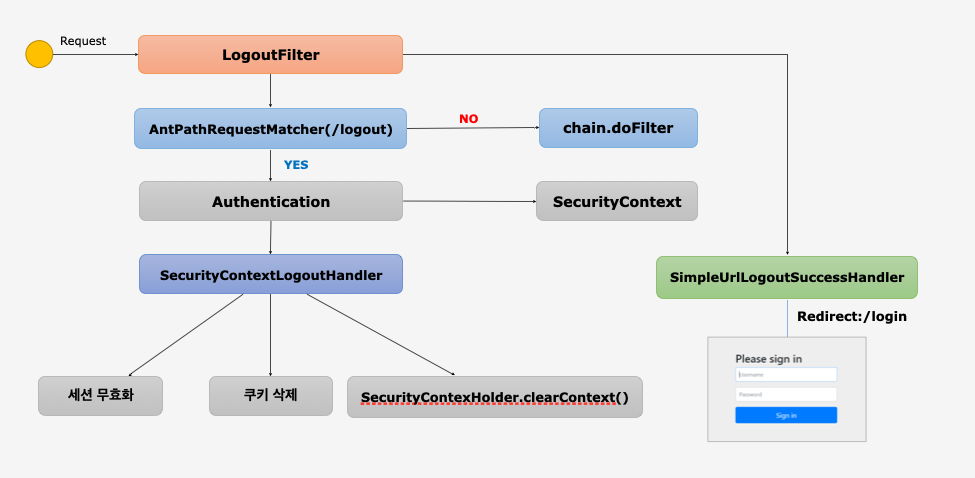
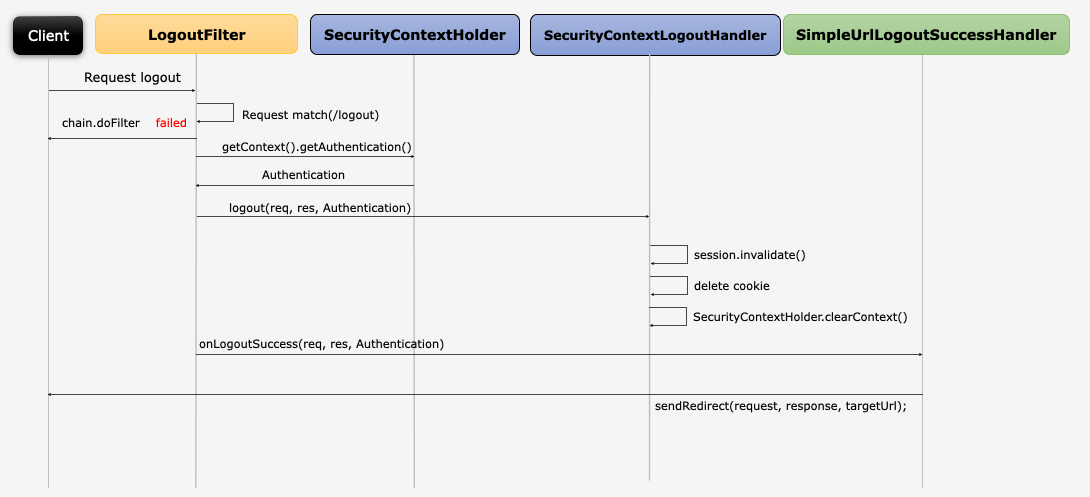
Logout, LogoutFilter
- 세션 저장소에 있는 세션을 없애고 쿠키 정보를 삭제
- 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉트
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login") // 여러가지 기본 구현체를 제공
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID", "remember-me")
.addLogoutHandler(logoutHandler()) // 여러가지 기본 구현체를 제공
.logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler())
}
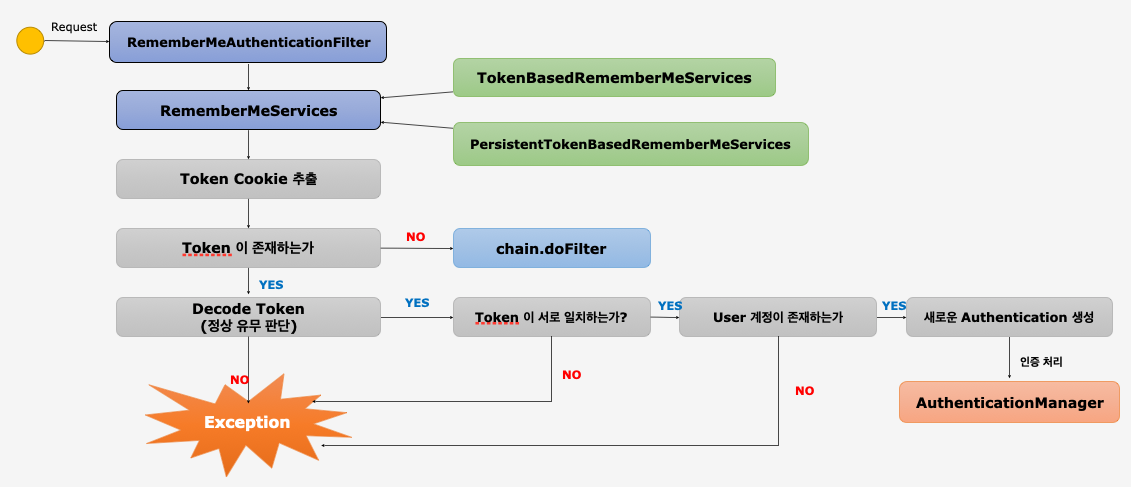
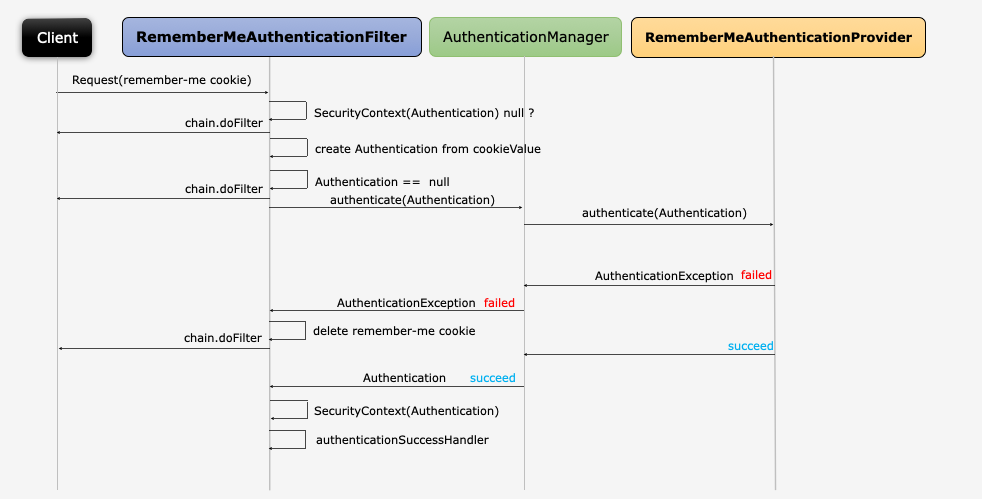
Remember Me & RememberMeAuthenticationFilter
- 세션이 만료되고 웹 브라우저가 종료된 후에도 어플리케이션이 사용자를 기억하는 기능
- Remember-Me 쿠키에 대한 Http 요청을 확인한 후 토큰 유효성 검사후
RememberMeAuthenticationToken를 생성해서 인증 과정을 진행한다.
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.rememberMe()
.rememberMeParameter(“remember”) // 기본 파라미터명은 remember-me
.tokenValiditySeconds(3600) // Default 는 14일
.alwaysRemember(true)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)
}
- 현재
SecurityContext에Authentication이 null이고 http 헤더에remember-me쿠키값이 있을때만 필터를 거친다. AuthenticationManager(ProvideManager)를 통한 인증이 성공하면RememberMeAuthenticationToken를SecurityContext에 저장한다.
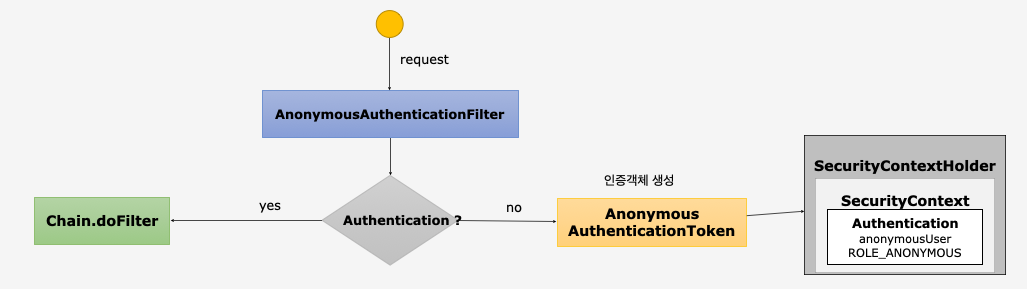
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- 익명사용자 인증 처리 필터
- 익명사용자와 인증 사용자를 구분해서 처리하기 위한 용도로 사용
- 화면에서 인증 여부를 구현할 때
isAnonymous()와isAuthenticated()로 구분해서 사용 - 인증객체를 세션에 저장하지 않는다.
동시 세션 제어 / 세션고정보호 / 세션 정책
동시 세션 제어
- 최대 세션 허용 개수 초과
- 이전 사용자 세션 만료
- 현재 사용자 인증 실패
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.sessionManagement()
.maximumSessions(1) // 최대 허용 가능 세션 수 , -1 : 무제한 로그인 세션 허용
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true) // 동시 로그인 차단함, false : 기존 세션 만료(default)
.invalidSessionUrl("/invalid")
.expiredUrl("/expired ")
}
세션 고정 보호 사용자
- 공격자가 본인의
JSESSIONID를 사용자 쿠키에 심어넣고 해당 사용자가 공격자의 쿠키로 로그인시에 공격자는 사용자의 정보 공유 가능
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.sessionManagement()
.sessionFixation()
.changeSessionId() // 기본값 // none, migrateSession, newSession
}
세션 정책
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.If_Required)
}
SessionCreationPolicy.Always: 스프링 시큐리티가 항상 세션 생성SessionCreationPolicy.If_Required: 스프링 시큐리티가 필요시 생성(기본값)SessionCreationPolicy.Never: 스프링 시큐리티가 생성하지 않지만 이미 존재하면 사용SessionCreationPolicy.Stateless: 스프링 시큐리티가 생성하지 않고 존재해도 사용하지 않음
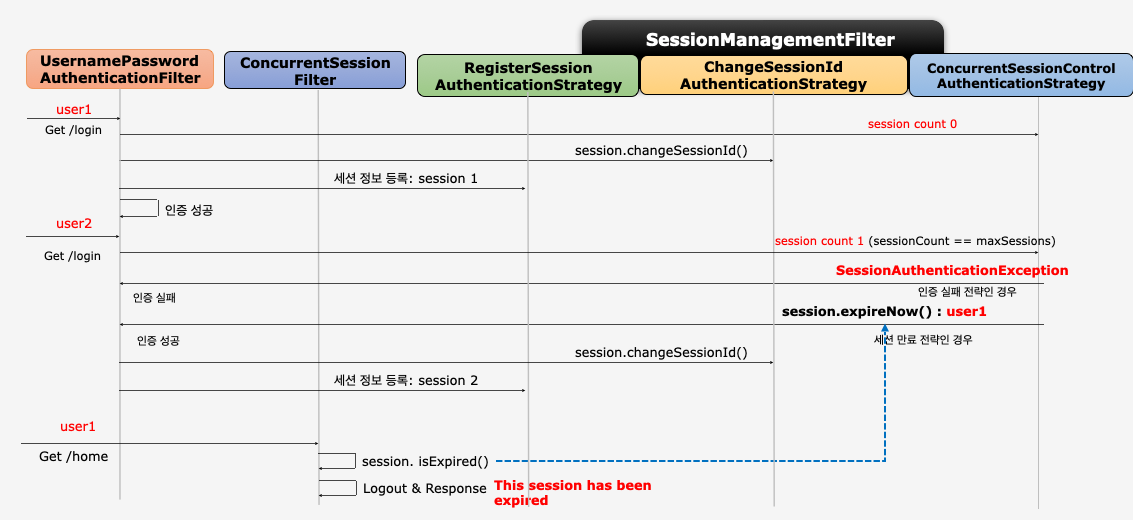
SessionManagementFilter & ConcurrentSessionFilter
SessionManagementFilter
- 세션 관리: 인증 시 사용자의 세션정보를 등록, 조회, 삭제 등의 세션 이력을 관리한다.
HttpSession이 아니라SessionRegistry의 기본 구현체인SessionRegistryImpl의Map<String, SessionInformation> sessionIds에 JSESSIONID를 키로 하고principal를 포함하는SessionInformation를 값으로 해서 저장한다. - 동시적 세션 제어: 동일 계정으로 접속이 허용되는 최대 세션수를 제한
- 세션 고정 보호: 인증 할 때마다 세션쿠키를 새로 발급하여 공격자의 쿠키 조작을 방지
- 세션 생성 정책: Always, If_Required, Never, Stateless
ConcurrentSessionFilter
- 매 요청 마다 현재 사용자의 세션 만료 여부 체크
- 세션이 만료로 설정되었을 경우 즉시 로그아웃 처리
session.isExpired() == true: 로그아웃 처리, 오류 페이지 응답
권한 설정 및 표현식
- 선언적 방식
- URL:
http.antMatchers("/users/**").hasRole(“USER") - Method:
@PreAuthorize("hasRole(‘USER’)")
- URL:
- 동적 방식 – DB 연동 프로그래밍
- URL
- Method
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/shop/login", "/shop/users/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers(" / shop / mypage").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/shop/admin/pay").access("hasRole('ADMIN')")
.antMatchers("/shop/admin/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') or hasRole('SYS')")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
}

ExceptionTranslationFilter & RequestCacheAwareFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter
- AuthenticationException
- 인증 예외 처리
AuthenticationEntryPoint호출: 로그인 페이지 이동, 401 오류 코드 전달 등- 인증 예외가 발생하기 전의 요청 정보를 저장
RequestCache- 사용자의 이전 요청 정보을 세션에 저장하고 이를 꺼내 오는 캐시 메카니즘SavedRequest- 사용자가 요청했던 request 파라미터 값들, 그 당시의 헤더값들 등이 저장
- AccessDeniedException
- 인가 예외 처리
AccessDeniedHandler에서 예외 처리하도록 제공
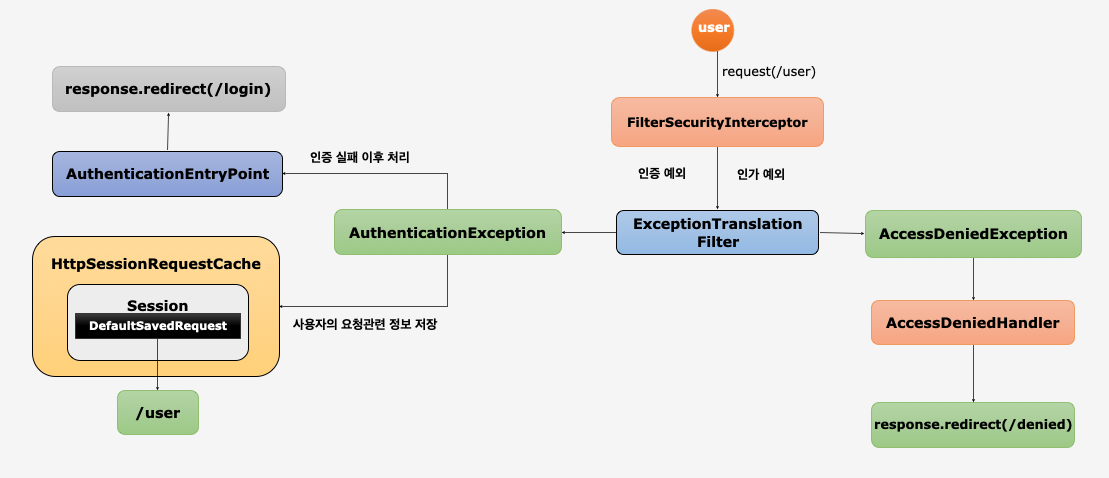
- 익명 사용자는
AccessDeniedException이 발생해도AuthenticationException으로 처리해서AuthenticationEntryPoint실행
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint())
.accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler())
}
RequestCacheAwareFilter
HttpSessionRequestCache에서 세션에 저장된 DefaultSavedRequest를 조회하고 있다면 캐쉬된 URI로 보낸다.
스프링 시큐리티 주요 아키텍처 이해
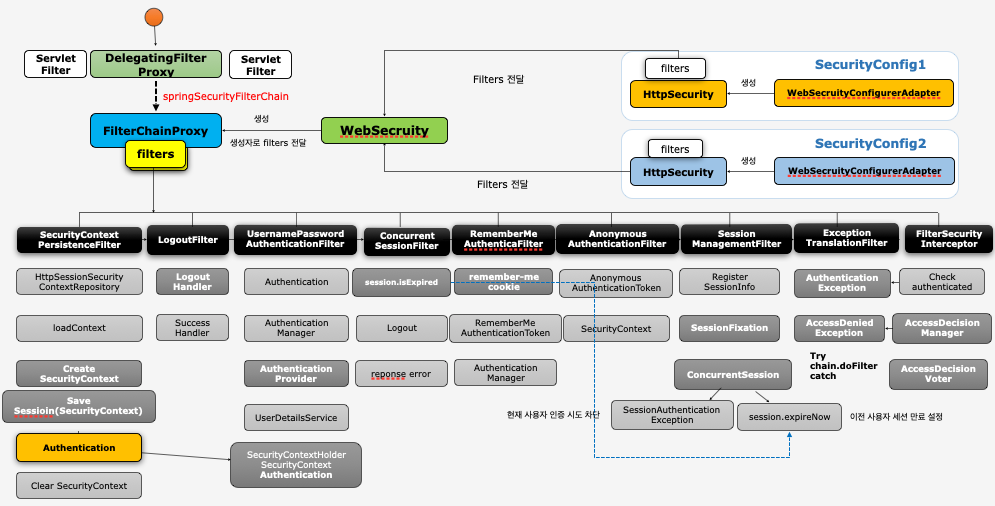
DelegatingFilterProxy & FilterChainProxy
DelegatingFilterProxy
- 서블릿 필터는 스프링에서 정의된 빈을 주입해서 사용할 수 없음
- 특정한 이름을 가진 스프링 빈을 찾아 그 빈에게 요청을 위임
springSecurityFilterChain이름으로 생성된 빈을ApplicationContext에서 찾아 요청을 위임
DelegatingFilterProxy는 서블리과 스프링의 징검다리 역할을 한다고 보면 된다.
FilterChainProxy
springSecurityFilterChain의 이름으로 생성되는 필터 빈DelegatingFilterProxy으로 부터 요청을 위임 받고 실제 보안 처리- 스프링 시큐리티 초기화 시 생성되는 필터들을 관리하고 제어
- 스프링 시큐리티가 기본적으로 생성하는 필터
- 설정 클래스에서 API 추가 시 생성되는 필터
- 사용자의 요청을 필터 순서대로 호출하여 전달
- 사용자정의 필터를 생성해서 기존의 필터 전.후로 추가 가능
- 마지막 필터까지 인증 및 인가 예외가 발생하지 않으면 보안 통과
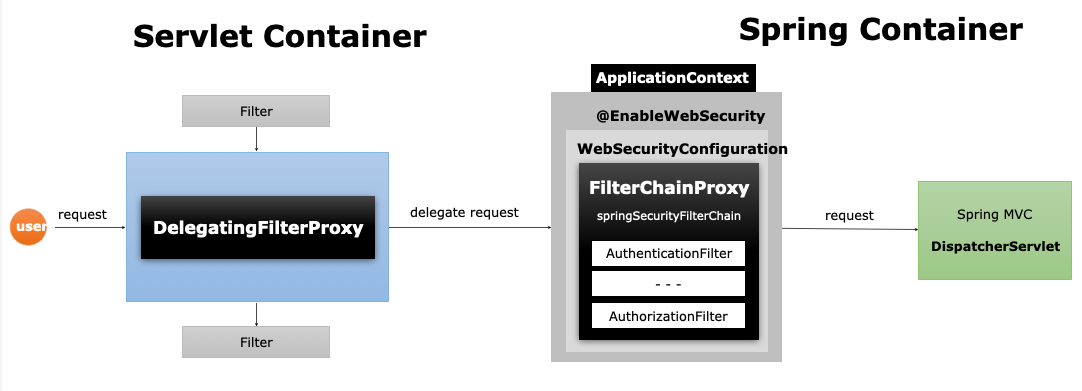
- spring secuirty 검증을 통과하면 이후 여러가지 서블릿 필터를 거친후
DispatcherServlet을 통해Controller에 매핑된다.
필터 초기화와 다중 보안 설정
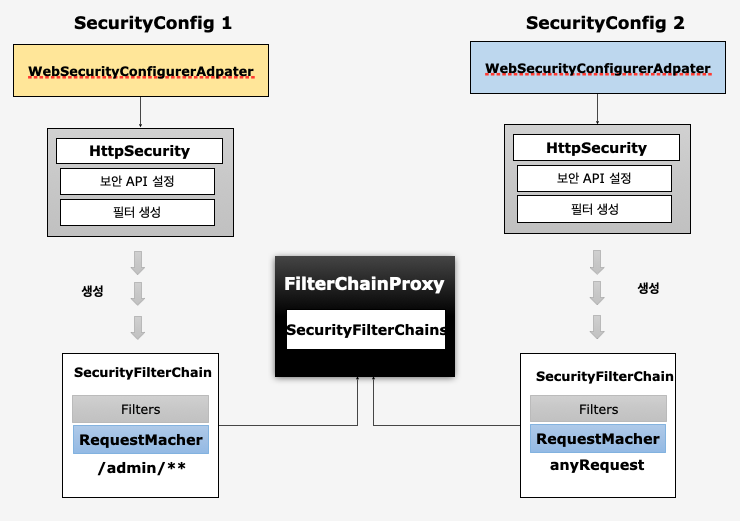
- 설정클래스 별로 보안 기능이 각각 작동
- 설정클래스 별로
RequestMatcher설정 (http.antMatcher("/admin/**")) - 설정클래스 별로 필터체인 생성
FilterChainProxy가 각 필터체인들 가지고 있음- 요청에 따라
RequestMatcher와 매칭되는 필터가 작동하도록 함 - 여러개의 필터체인을 생성하기 위해서는 여러개의 설정 클래스를 작성해야 한다.
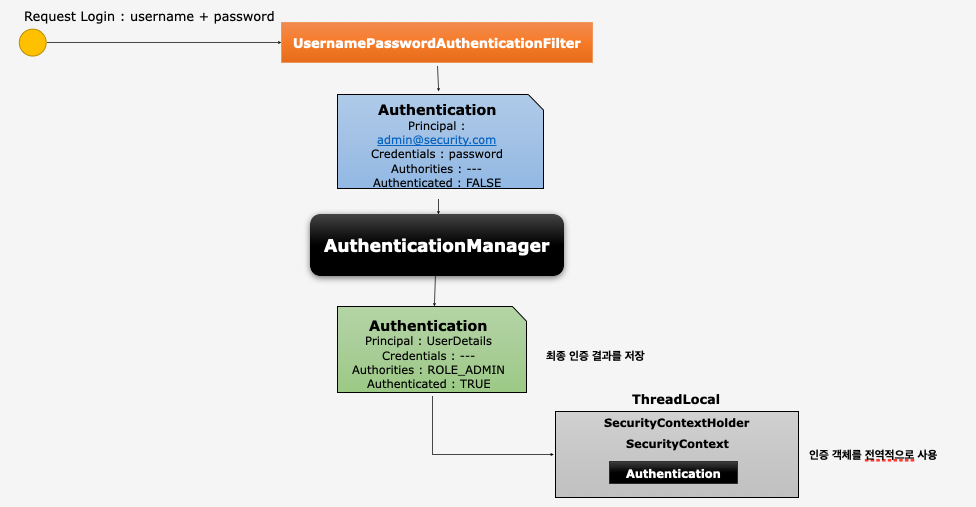
Authentication
- 사용자의 인증 정보를 저장하는 토큰 개념
- 인증 시 id와 password를 담고 인증 검증을 위해 전달되어 사용된다.
- 인증 후 최종 인증 결과 (user 객체, 권한정보) 를 담고
SecurityContext에 저장되어 전역적으로 참조가 가능하다. (Authentication authentication = SecurityContexHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()) - 구조
principal: 사용자 아이디 혹은User객체를 저장credentials: 사용자 비밀번호authorities: 인증된 사용자의 권한 목록details: 인증 부가 정보Authenticated: 인증 여부
SecurityContextHolder, SecurityContext
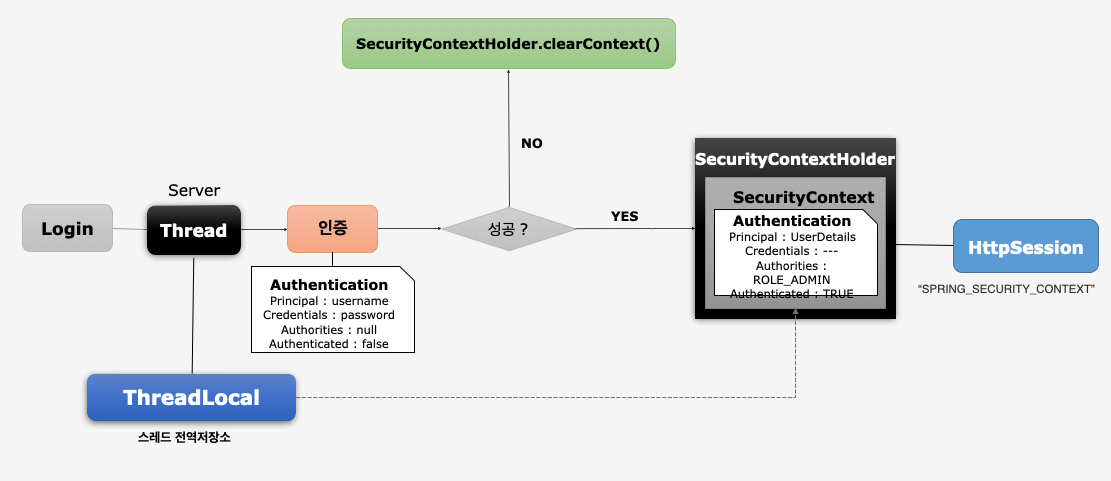
SecurityContext
Authentication객체가 저장되는 보관소로 필요 시 언제든지Authentication객체를 꺼내어 쓸 수 있도록 제공되는 인터페이스ThreadLocal에 저장되어 아무 곳에서나 참조가 가능하도록 설계함- 인증이 완료되면
HttpSession에 저장되어 어플리케이션 전반에 걸쳐 전역적인 참조가 가능하다.
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContext객체 저장 방식MODE_THREADLOCAL: 스레드당SecurityContext객체를 할당, 기본값MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL: 메인 스레드와 자식 스레드에 관하여 동일한SecurityContext를 유지MODE_GLOBAL: 응용 프로그램에서 단 하나의SecurityContext를 저장한다.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext():SecurityContext기존 정보 초기화
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
SecurityContext객체의 생성, 저장, 조회- 익명 사용자
- 새로운
SecurityContext객체를 생성하여SecurityContextHolder에 저장 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter에서AnonymousAuthenticationToken객체를SecurityContext에 저장
- 새로운
- 인증 시
- 새로운
SecurityContext객체를 생성하여SecurityContextHolder에 저장 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서 인증 성공 후SecurityContext에UsernamePasswordAuthentication객체를SecurityContext에 저장- 인증이 최종 완료되면
HttpSession에SecurityContext를 저장
- 새로운
- 인증 후
Session에서SecurityContext꺼내어SecurityContextHolder에서 저장SecurityContext안에Authentication객체가 존재하면 계속 인증을 유지한다.
- 최종 응답시 공통:
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext()
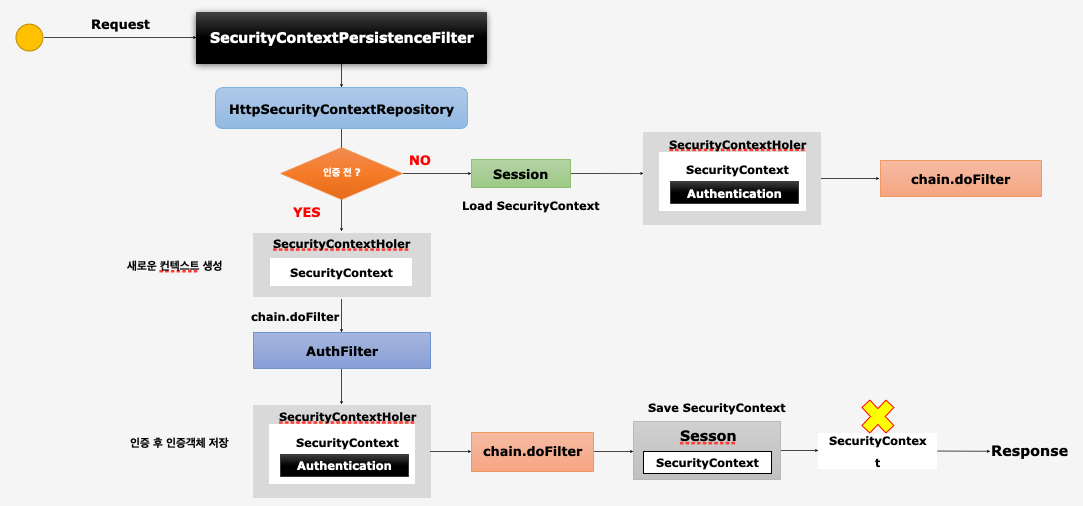
HttpSecurityContextRepository는 세션이 존재하면 기존SecurityContext를 반환하고 세션이 없다면 새로운SecurityContext를 생성해서 반환한다.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter는 반환된SecurityContext를SecurityContextHolder에 담고 그 다음 필터를 호출한다.- 응답시에는
AnonymousAuthenticationToken이 아니라면SecurityContext를 세션에 저장하고 응답한다.
Authentication Flow
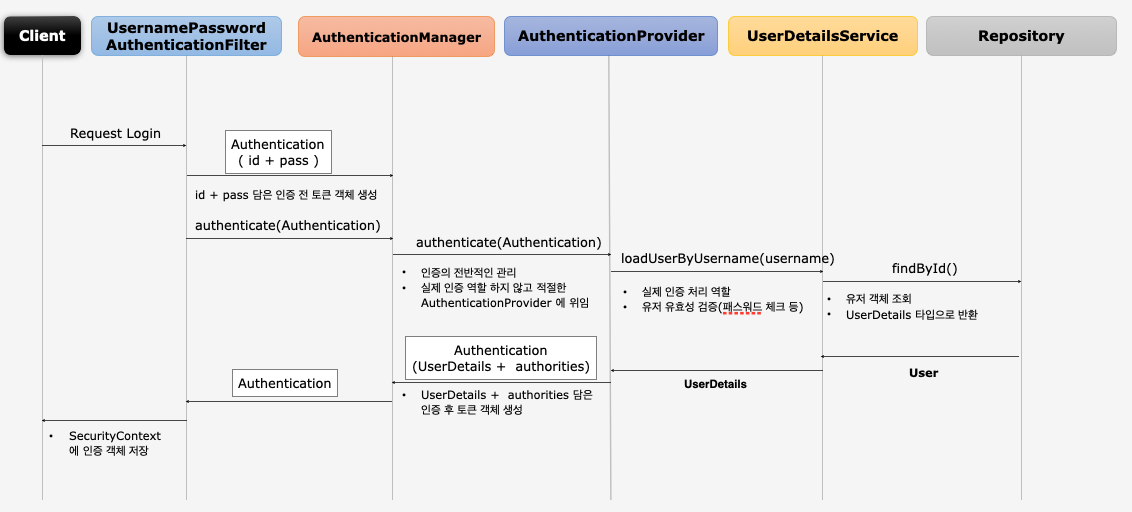
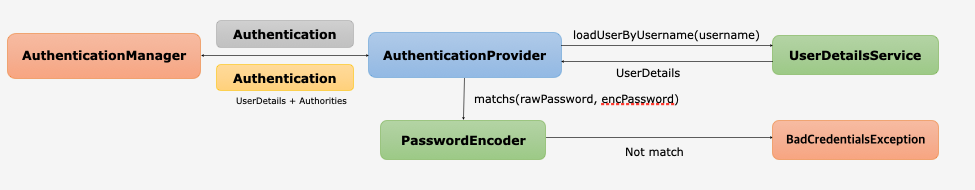
AuthenticationManager
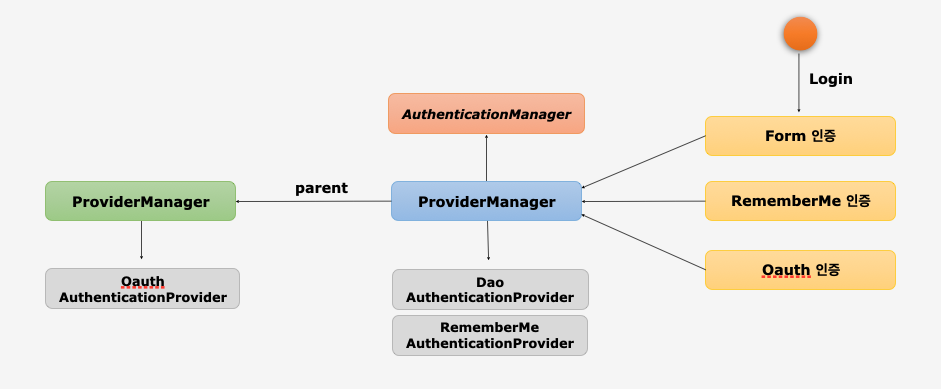
AuthenticationProvider목록 중에서 인증 처리 요건에 맞는AuthenticationProvider를 찾아 인증 처리를 위임한다.- 부모
ProviderManager를 설정하여AuthenticationProvider를 계속 탐색 할 수 있다. - 스프링 시큐리티 초기화 과정에서 부모 관계를 적절히 커스텀하면 커스텀한 모든
AuthenticationProvider탐색이 가능하다.
AuthenticationProvider
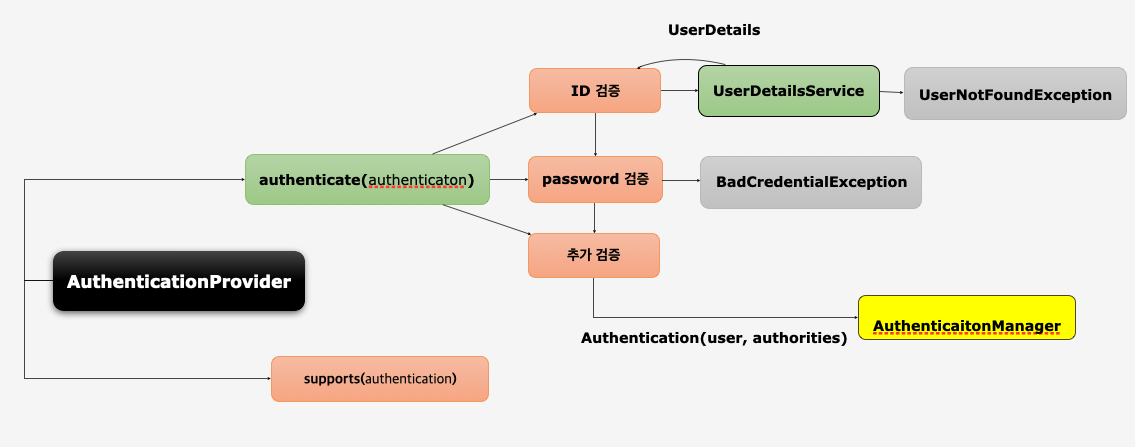
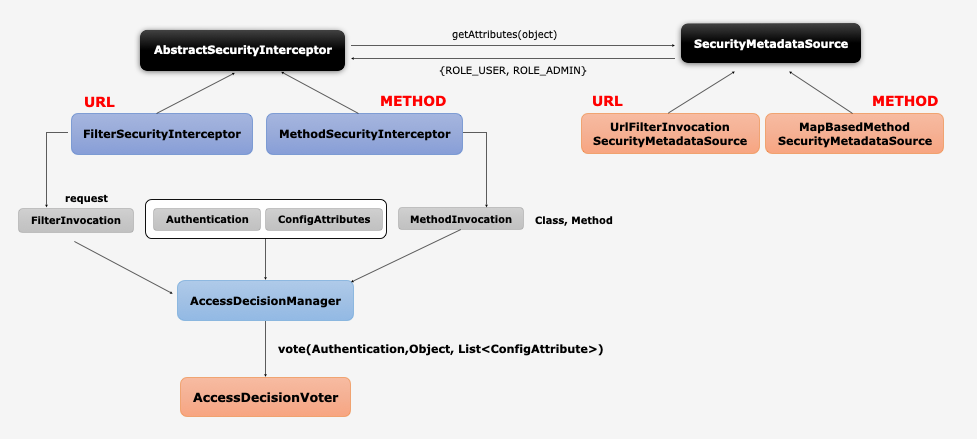
Authorization, FilterSecurityInterceptor
Authorization
- 스프링 시큐리티가 지원하는 권한 계층
- 웹 계층: URL 요청에 따른 메뉴 혹은 화면단위의 레벨 보안
- 서비스 계층: 화면 단위가 아닌 메소드 같은 기능 단위의 레벨 보안
- 도메인 계층(Access Control List, 접근제어목록): 객체 단위의 레벨 보안
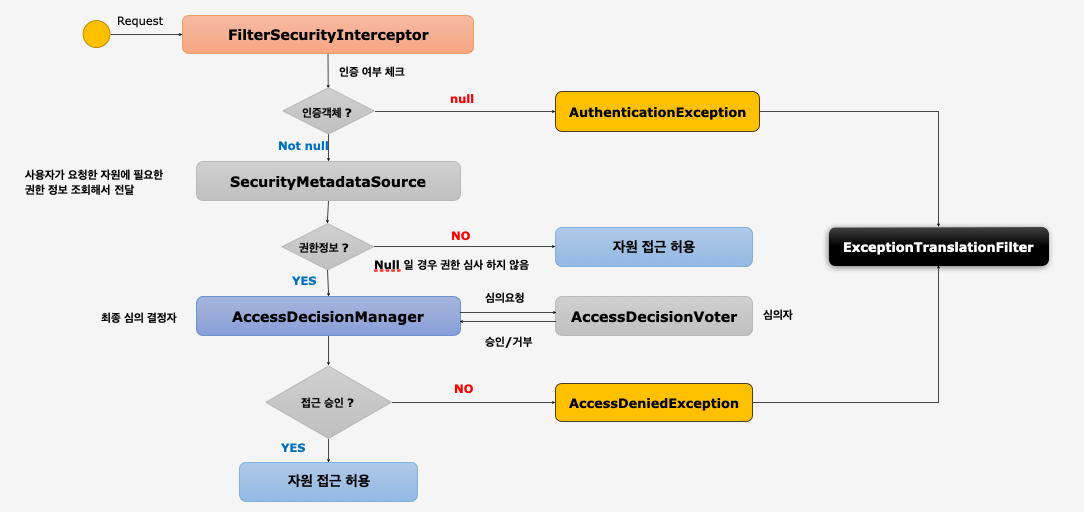
FilterSecurityInterceptor
- 마지막에 위치한 필터로써 인증된 사용자에 대하여 특정 요청의 승인 / 거부 여부를 최종적으로 결정
- 인증 객체 없이 보호자원에 접근을 시도할 경우
AuthenticationException을 발생 - 인증후 자원에 접근 가능한 권한이 존재하지 않을 경우
AccessDeniedException을 발생, 여러번 말하지만 익명 사용자의 경우AuthenticationException로 처리하여AuthenticationEntryPoint실행 - 권한 제어 방식중 HTTP 자원의 보안을 처리하는 필터
- 권한처리를
AccessDecisionManager에게 맡김
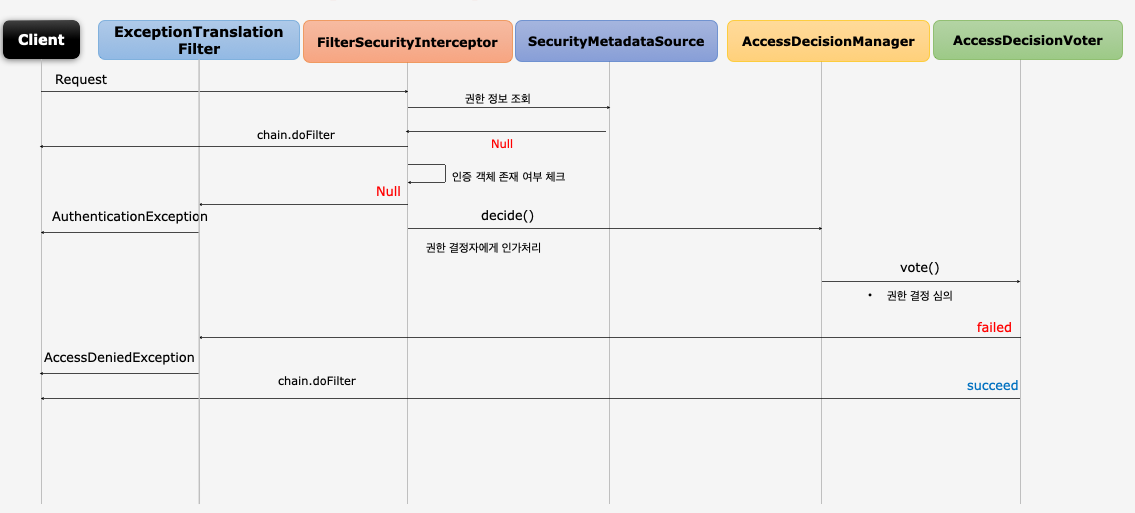
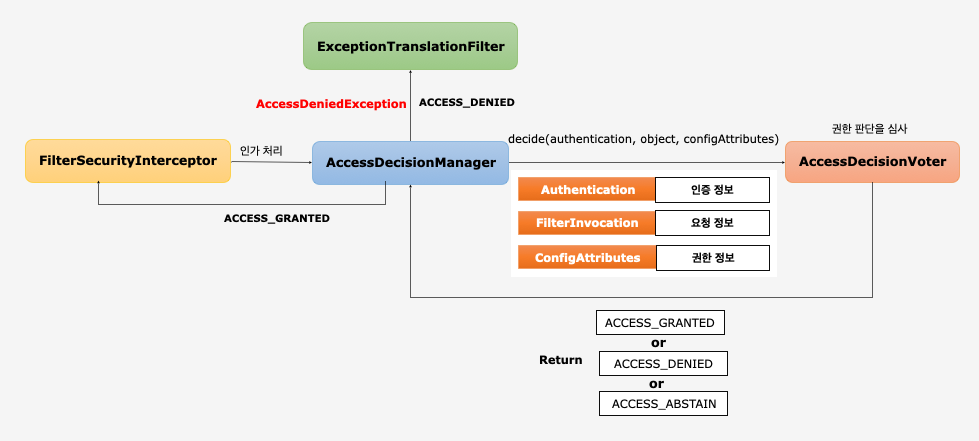
AccessDecisionManager, AccessDecisionVoter
AccessDecisionManager
- 인증 정보, 요청정보, 권한정보를 이용해서 사용자의 자원접근을 허용할 것인지 거부할 것인지를 최종 결정하는 주체
- 여러 개의 Voter 들을 가질 수있으며 Voter 들로부터 접근허용, 거부, 보류에 해당하는 각각의 값을 리턴받고 판단 및 결정
- 최종 접근 거부 시 예외 발생
- 접근결정의 세가지 유형
- AffirmativeBased: 여러개의 Voter 클래스 중 하나라도 접근 허가로 결론을 내면 접근 허가로 판단한다.
- ConsensusBased: 다수표(승인 및 거부)에 의해 최종 결정을 판단한다. 동수일경우 기본은 접근허가이나
allowIfEqualGrantedDeniedDecisions을false로 설정할 경우 접근거부로 결정된다. - UnanimousBased: 모든 Voter가 만장일치로 접근을 승인해야 하며 그렇지 않은 경우 접근을 거부한다.
AccessDecisionVoter
- Voter가 권한 부여 과정에서 판단하는 자료
- Authentication - 인증 정보(
user,anonymous,admin) - FilterInvocation – 요청 정보(
antMatcher("/user")) - ConfigAttributes - 권한 정보 (
hasRole("USER"))
- Authentication - 인증 정보(
- 결정 방식
ACCESS_GRANTED: 접근허용(1)ACCESS_DENIED: 접근 거부(-1)ACCESS_ABSTAIN: 접근 보류(0)
- 커스텀한
AccessDecisionVoter추가도 가능하다.
스프링 시큐리티 필터 및 아키텍처 정리
실전프로젝트 -인증 프로세스 Form 인증 구현
CustomAuthenticationProvider
로그아웃
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/logout")
public String logout(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null) {
new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, authentication);
}
return "redirect:/login";
}
}
- 로그아웃 방법
<form>태그를 사용해서 POST로 요청<a>태크를 사용해서 GET으로 요청 –SecurityContextLogoutHandler활용
WebAuthenticationDetails, AuthenticationDetailsSource
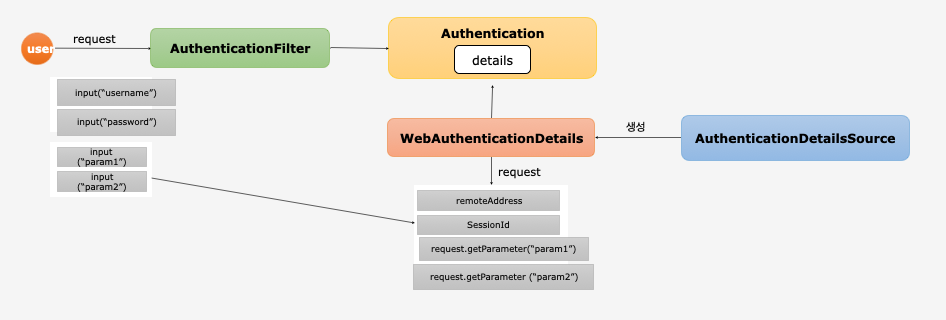
- WebAuthenticationDetails(클래스)
- 인증 과정 중 전달된 데이터를 저장
Authentication의details속성에 저장- 상속으로 커스텀한 클래스를 만들수 있다. 따라서 기본적으로 갖고 있는 프로퍼티외 파라미터 등 인증 단계에서 필요한 데이터를 추가할 수 있다.
- AuthenticationDetailsSource(인터페이스)
WebAuthenticationDetails객체를 생성- 인터페이스 구현으로 커스텀한 클래스를 만들 수 있다.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Autowired
private AuthenticationDetailsSource authenticationDetailsSource;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login_proc")
.authenticationDetailsSource(authenticationDetailsSource)
.defaultSuccessUrl("/");
}
...
}
CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
this.setDefaultTargetUrl("/");
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, targetUrl);
} else {
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, this.getDefaultTargetUrl());
}
}
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
...
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler)
...
}
CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서 발생한UsernameNotFoundException,BadCredentialsException과 같은 예외를 처리한다.
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
String errorMessage = "Invalid Username or Password";
if (exception instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
errorMessage = "Invalid Username or Password";
} else if (exception instanceof InsufficientAuthenticationException) {
errorMessage = "Invalid Secret Key";
}
this.setDefaultFailureUrl("/login?error=true&exception=" + errorMessage);
super.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, exception);
}
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
...
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler)
...
}
실전프로젝트 - 인증 프로세스 Ajax 인증 구현
흐름 및 개요
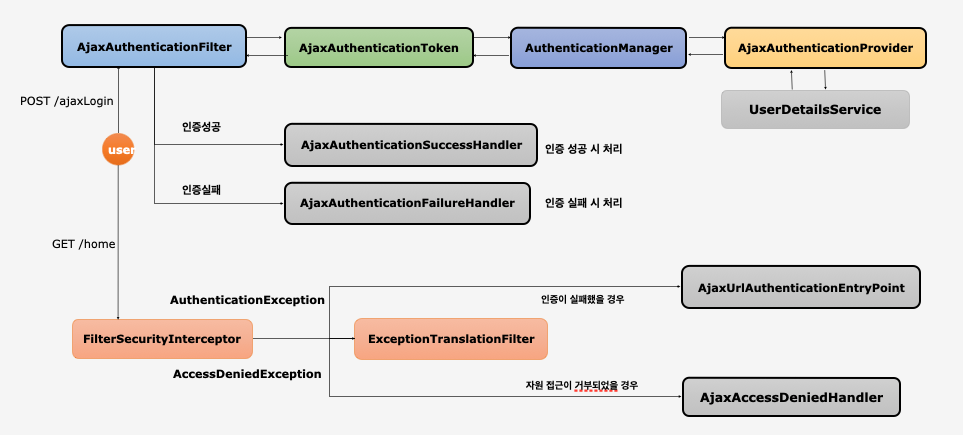
AjaxAuthenticationFilter
public class AjaxLoginProcessingFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter { // config에서 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 앞에 추가 필요
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public AjaxLoginProcessingFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/api/login"));
}
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
if (!isAjax(request)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Authentication is not supported");
}
AccountDto accountDto = objectMapper.readValue(request.getReader(), AccountDto.class);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(accountDto.getUsername()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(accountDto.getPassword())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("username or Password is empty");
}
AjaxAuthenticationToken ajaxAuthenticationToken = new AjaxAuthenticationToken(accountDto.getUsername(), accountDto.getPassword());
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(ajaxAuthenticationToken); // config에서 AuthenticationManager 설정 필요
}
private boolean isAjax(HttpServletRequest request) {
if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(request.getHeader("X-Requested-With"))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class AjaxAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
public AjaxAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
public AjaxAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return this.credentials;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
@Override
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException {
Assert.isTrue(!isAuthenticated,
"Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
@Override
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
this.credentials = null;
}
}
- 기존
SecurityConfig와 다른 새로운AjaxSecurityConfig클래스를 생성하고 적절히 오버라이딩한다. 그러면 필터체인이 2개가 생성되고 각 config에서 설정한mvcMatcher()에 따라 체인이 선택된다.
AjaxAuthenticationProvider
public class AjaxAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
@Transactional
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
AccountContext accountContext = (AccountContext) userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(password, accountContext.getAccount().getPassword())) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("BadCredentialsException");
}
FormWebAuthenticationDetails details = (FormWebAuthenticationDetails) authentication.getDetails();
String secretKey = details.getSecretKey();
if (secretKey == null || !secretKey.equals("secret")) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException("InsufficientAuthenticationException");
}
return new AjaxAuthenticationToken(accountContext, null, accountContext.getAuthorities());
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return AjaxAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(ajaxAuthenticationProvider());
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider ajaxAuthenticationProvider() {
return new AjaxAuthenticationProvider();
}
AjaxAuthenticationSuccessHandler, AjaxAuthenticationFailureHandler
AjaxAuthenticationSuccessHandler
public class AjaxAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
AccountContext principal = (AccountContext) authentication.getPrincipal();
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
objectMapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), principal.getAccount());
}
}
AjaxAuthenticationFailureHandler
public class AjaxAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
String errorMsg = "Invalid Username or Password";
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
if (exception instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
errorMsg = "Invalid Username or Password";
} else if (exception instanceof InsufficientAuthenticationException) {
errorMsg = "Invalid Secret Key";
}
objectMapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), errorMsg);
}
}
@Bean
public AjaxLoginProcessingFilter ajaxLoginProcessingFilter() throws Exception {
AjaxLoginProcessingFilter ajaxLoginProcessingFilter = new AjaxLoginProcessingFilter();
ajaxLoginProcessingFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
ajaxLoginProcessingFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler());
ajaxLoginProcessingFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler());
return ajaxLoginProcessingFilter;
}
AjaxLoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint, AjaxAccessDeniedHandler
AjaxLoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint
public class AjaxLoginAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, "UnAuthorized");
}
}
AjaxAccessDeniedHandler
public class AjaxAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN, "Access is denied");
}
}
실전프로젝트 - 인가 프로세스 DB 연동 웹 계층 구현
개요
- DB와 연동하여 자원 및 권한을 설정하고 제어함으로 동적 권한 관리가 가능하도록 한다.
- 설정 클래스 소스에서 권한 관련 코드 모두 제거 ex)
antMatcher(“/user”).hasRole(“USER") - 관리자 시스템 구축
- 회원 관리 – 권한 부여
- 권한 관리 – 권한 생성, 삭제
- 자원 관리 – 자원 생성, 삭제, 수정, 권한매핑
- 권한 계층 구현
- URL – Url 요청 시 인가 처리
- Method – 메소드 호출 시 인가 처리
- Method
- Pointcut
Url 방식 - 주요 아키텍처 이해
http.antMatchers(“/user”).access(“hasRole(‘USER’)”)- 사용자(인증 정보)가
/user(요청 정보) 자원에 접근하기 위해서는ROLE_USER(권한 정보) 권한이 필요하다
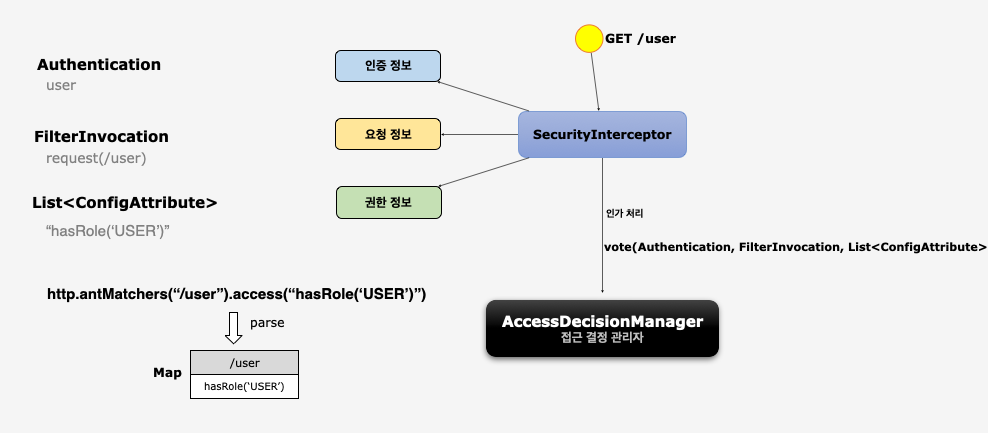
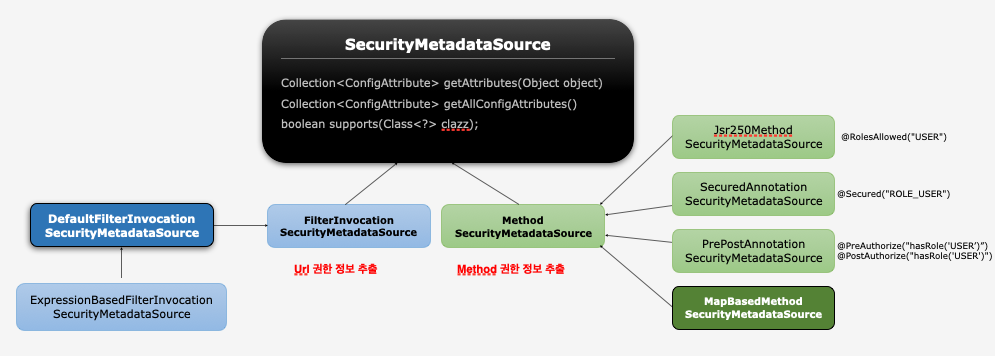
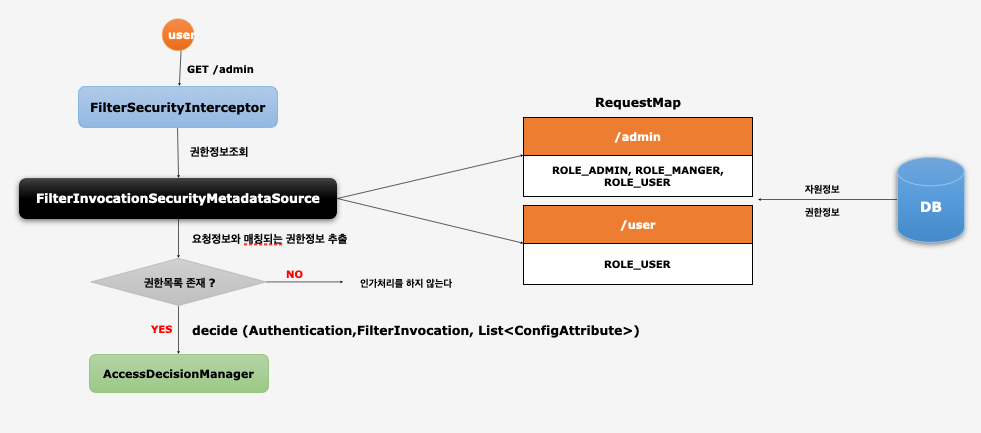
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
- 사용자가 접근하고자 하는 Url 자원에 대한 권한 정보 추출
AccessDecisionManager에게 전달하여 인가처리 수행- DB로부터 자원 및 권한정보를 매핑하여 맵으로 관리
- 사용자의 매 요청마다 요청정보에 매핑된 권한 정보 확인
public class UrlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
private LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> requestMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequest();
if (requestMap != null) {
for (Map.Entry<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> entry : requestMap.entrySet()) {
RequestMatcher matcher = entry.getKey();
if (matcher.matches(request)) {
return entry.getValue();
}
}
}
return null; // null을 반환하면 인가처리를 하지 않는다.
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
Set<ConfigAttribute> allAttributes = new HashSet<>();
this.requestMap.values().forEach(allAttributes::addAll);
return allAttributes;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return FilterInvocation.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@Order(1)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Bean
public FilterSecurityInterceptor customFilterSecurityInterceptor() throws Exception {
FilterSecurityInterceptor filterSecurityInterceptor = new FilterSecurityInterceptor();
filterSecurityInterceptor.setSecurityMetadataSource(urlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource());
filterSecurityInterceptor.setAccessDecisionManager(affirmativeBased());
filterSecurityInterceptor.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
return filterSecurityInterceptor;
}
@Bean
public FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource urlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource() {
return new UrlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource();
}
@Bean
public AccessDecisionManager affirmativeBased() {
AffirmativeBased affirmativeBased = new AffirmativeBased(getAccessDecisionVoters());
return affirmativeBased;
}
private List<AccessDecisionVoter<?>> getAccessDecisionVoters() {
return Arrays.asList(new RoleVoter());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
...
http
.addFilterBefore(customFilterSecurityInterceptor(), FilterSecurityInterceptor.class);
...
}
}
- 기존에 등록된
FilterSecurityInterceptor의 경우 커스텀한FilterSecurityInterceptor에서 인가처리를 하게 되면 인가처리를 진행하지 않고 그 다음 필터로 넘기게 된다.
public void invoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (isApplied(filterInvocation) && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
return;
}
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (filterInvocation.getRequest() != null && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
filterInvocation.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(filterInvocation); // 인가 로직
try {
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
Map 기반 DB 연동
DB와 연동하여 LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> resourceMap를 생성하는 service를 만든다. 해당 서비스를 이용하여 resourceMap를 빈으로 생성하는 FactoryBean 구현체를 생성하고 UrlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 생성시에 resourceMap를 주입한다. FilterSecurityInterceptor에 해당 UrlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource을 주입하고 FilterSecurityInterceptor 필터를 기존 FilterSecurityInterceptor 필터 앞에 추가하면 된다. 여기서 핵심은 Resources와 Role 테이블을 설계하고 조인으로 원하는 결과를 가져오는 것이다. rquest pattern과 mvaPattern이 매칭되는 순서가 중요하므로 order 프로퍼티를 정해 정렬하여 데이터를 가져오고 기본 HashMap이 아닌 순서가 보장되는 LinkedHashMap을 사용한다.
public class UrlResourcesMapFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>>> {
private SecurityResourceService securityResourceService;
private LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> resourceMap;
public void setSecurityResourceService(SecurityResourceService securityResourceService) {
this.securityResourceService = securityResourceService;
}
@Override
public LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> getObject() throws Exception {
if (resourceMap == null) {
init();
}
return resourceMap;
}
private void init() {
resourceMap = securityResourceService.getResourceList();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return LinkedHashMap.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
인가처리 실시간 반영하기
public class UrlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
private LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> requestMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
...
public void reload() { // controller와 매핑하여 trigger 가능
LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> reloadedMap = securityResourceService.getResourceList();
Iterator<Map.Entry<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>>> iterator = reloadedMap.entrySet().iterator();
requestMap.clear();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<RequestMatcher, List<ConfigAttribute>> entry = iterator.next();
reloadedMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
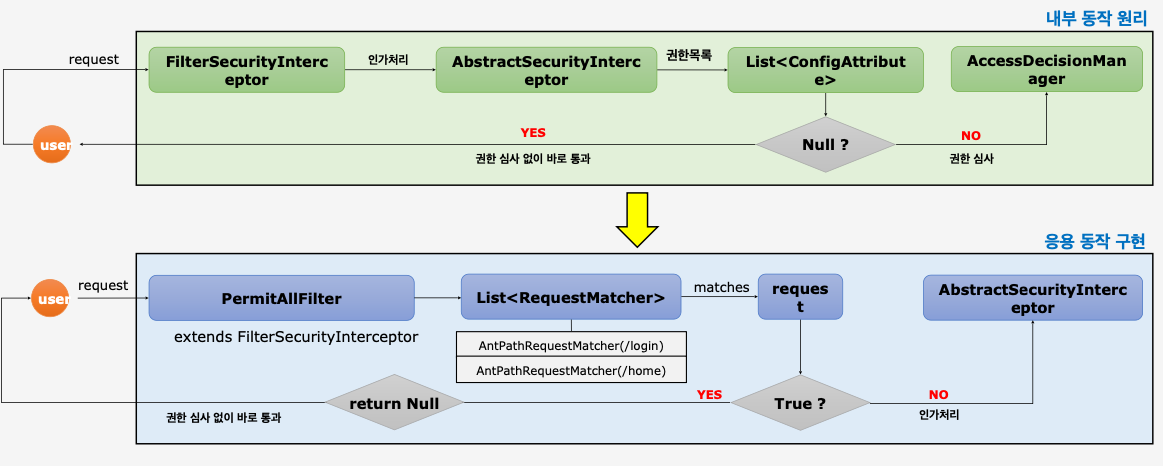
PermitAllFilter 구현
public class PermitAllFilter extends FilterSecurityInterceptor {
private static final String FILTER_APPLIED = "__spring_security_filterSecurityInterceptor_filterApplied";
private boolean observeOncePerRequest = true;
private List<RequestMatcher> permitAllRequestMatchers = new ArrayList<>();
public PermitAllFilter(String... permitAllResources) {
for (String permitAllResource : permitAllResources) {
permitAllRequestMatchers.add(new AntPathRequestMatcher(permitAllResource));
}
}
private boolean isApplied(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) {
return (filterInvocation.getRequest() != null)
&& (filterInvocation.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null);
}
@Override
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
boolean permitAll = false;
HttpServletRequest request = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequest();
for (RequestMatcher requestMatcher : permitAllRequestMatchers) {
if (requestMatcher.matches(request)) {
permitAll = true;
break;
}
}
if (permitAll) {
return null;
}
return super.beforeInvocation(object);
}
@Override
public void invoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (isApplied(filterInvocation) && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
return;
}
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (filterInvocation.getRequest() != null && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
filterInvocation.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(filterInvocation);
try {
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
- permiAll 리소스의 경우 불필요한 로직을 타는것을 방지하기 위해
permitAllRequestMatchers에 매칭된다면 인가 로직을 태우지 않고null을 반환하고 그 다음 필터를 호출하게 된다. 물론 그 다음 필터는FilterSecurityInterceptor인데 이 역시 전에서 말한대로 한번 이미 필터를 거쳤으므로 로직을 태우지 않고 바로 다음 필터를 호출한다.
계층 권한 적용하기
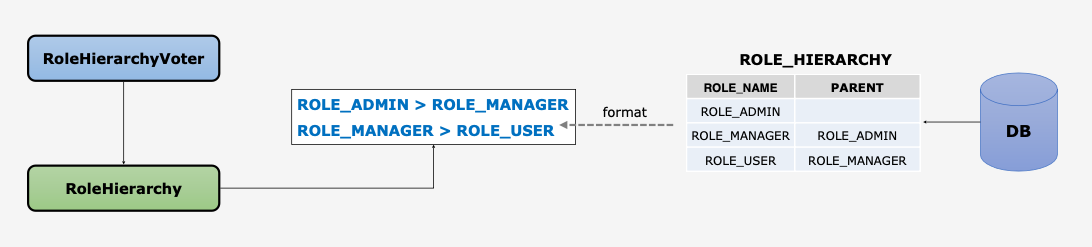
- RoleHierarchy
- 상위 계층 Role은 하위 계층 Role의 자원에 접근 가능함
ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_MANAGER > ROLE_USER일 경우ROLE_ADMIN만 있으면 하위 ROLE의 권한을 모두 포함한다.
- RoleHierarchyVoter
- RoleHierarchy를 생성자로 받으며 이 클래스에서 설정한 규칙이 적용되어 심사함
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@Order(1)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public FilterSecurityInterceptor customFilterSecurityInterceptor() throws Exception {
FilterSecurityInterceptor filterSecurityInterceptor = new FilterSecurityInterceptor();
filterSecurityInterceptor.setSecurityMetadataSource(urlFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource());
filterSecurityInterceptor.setAccessDecisionManager(affirmativeBased());
filterSecurityInterceptor.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean());
return filterSecurityInterceptor;
}
@Bean
public AccessDecisionManager affirmativeBased() {
AffirmativeBased affirmativeBased = new AffirmativeBased(getAccessDecisionVoters());
return affirmativeBased;
}
private List<AccessDecisionVoter<?>> getAccessDecisionVoters() {
List<AccessDecisionVoter<? extends Object>> accessDecisionVoters = new ArrayList<>();
accessDecisionVoters.add(roleVoter());
return accessDecisionVoters;
}
@Bean
public AccessDecisionVoter<? extends Object> roleVoter() {
RoleHierarchyVoter roleHierarchyVoter = new RoleHierarchyVoter(roleHierarchy());
return roleHierarchyVoter;
}
@Bean
public RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy() {
RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl();
return roleHierarchy;
}
}
@Component
public class SecurityInitializer implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy;
@Autowired
private RoleHierarchyService roleHierarchyService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
String allHierarchy = roleHierarchyService.findAllHierarchy();
roleHierarchy.setHierarchy(allHierarchy);
}
}
RoleHierarchyVoter를 추가하는 것 외에 기존WebExpressionVoter에 위계를 이해할 수 있는handler를 커스터마이징 해도 된다.
아이피 접속 제한하기
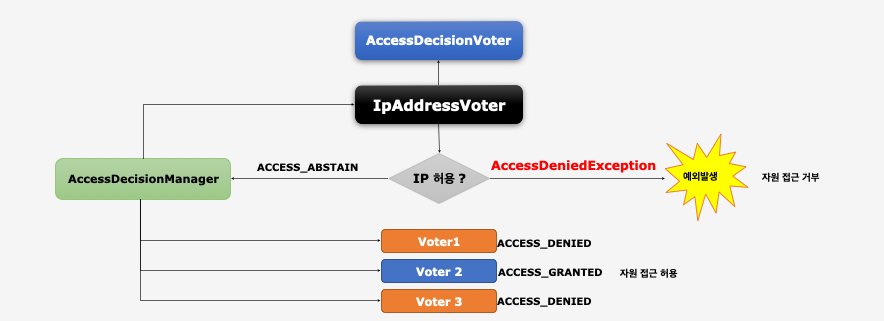
- 특정한 IP만 접근이 가능하도록 심의하는 Voter 추가
- Voter 중에서 가장 먼저 심사하도록 하여 허용된 IP일 경우에만 최종 승인 및 거부 결정을 하도록 한다.
- 허용된 IP면
ACCESS_GRANTED가 아닌ACCESS_ABSTAIN을 리턴해서 추가 심의를 계속 진행하도록 한다. - 허용된 IP가 아니면
ACCESS_DENIED를 리턴하지 않고 즉시 예외 발생하여 최종 자원 접근 거부
public class IpAddressVoter implements AccessDecisionVoter {
private SecurityResourceService securityResourceService;
public IpAddressVoter(SecurityResourceService securityResourceService) {
this.securityResourceService = securityResourceService;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class clazz) {
return true;
}
@Override
public int vote(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection collection) {
WebAuthenticationDetails details = (WebAuthenticationDetails) authentication.getDetails();
String remoteAddress = details.getRemoteAddress();
List<String> accessIpList = securityResourceService.getAccessIpList();
for (String ipAddress : accessIpList) {
if (remoteAddress.equals(ipAddress)) {
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("Invalid IpAddress");
}
}
- DB에서 허용되는 IP 목록을 가져오고 매칭시켜 본다.
여러 종류의 voter
AccessDecisionVoter 구현체는 다양하다. 기본적으로 사용되는 WebExpressionVoter 뿐만 아니라 RoleVoter, RoleHierarchyVoter 등 종류가 다양하다. 각 voter에서 지원하는 ConfigAttribute 구현체의 종류가 다르며 voter안에서 권한 검증 로직 또한 다르다. 따라서 user에 저장된 authorities와 ConfigAttribute 등을 종합적으로 고려하여 voter를 커스터마이징 해야한다.
실전프로젝트 - 인가 프로세스 DB 연동 서비스 계층 구현
개요
- 서비스 계층의 인가처리 방식
- 화면, 메뉴 단위가 아닌 기능 단위로 인가처리
- 메소드 처리 전.후로 보안 검사 수행하여 인가처리
- AOP 기반으로 동작
- 프록시와 어드바이스로 메소드 인가처리 수행
- 보안 설정 방식
- 어노테이션 권한 설정 방식
@PreAuthorize(“hasRole(‘USER’)”), @PostAuthorize(“hasRole(‘USER’)”), @Secured(“ROLE_USER”)
- 맵 기반 권한 설정 방식
- 맵 기반 방식으로 외부와 연동하여 메소드 보안 설정 구현
- 어노테이션 권한 설정 방식
어노테이션 권한 설정
- 보안이 필요한 메소드에 설정한다.
- @PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize
- SpEL 지원
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_USER’) and (#account.username == principal.username)")- PrePostAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource가 담당
- @Secured, @RolesAllowed
- SpEL 미지원
@Secured ("ROLE_USER"),@RolesAllowed("ROLE_USER")- SecuredAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource, Jsr250MethodSecurityMetadataSource가 담당
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)

GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration에서@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity설정을 기반으로PrePostAnnotationSecurityMetadataSource등으로 이루어진 list를 담은DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource를 반환한다.MethodSecurityInterceptor에서는DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource를 이용하여 인가 로직을 태운 다음 실제 호출된 메소드를 호출한다. 즉MethodInterceptor는MethodInterceptor를 구현하고 있다.DelegatingMethodSecurityMetadataSource에서는List<MethodSecurityMetadataSource> methodSecurityMetadataSources를 돌아가면서method와targetClass의 정보를 이용하여Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes를 반환한다.(캐시용 맵이 존재한다.)
주요 아키텍처
- 인가 처리를 위한 초기화 과정과 진행
- 초기화 과정
- 초기화 시 전체 빈을 검사하면서 보안이 설정된 메소드가 있는지 탐색
- 빈의 프록시 객체를 생성
- 보안 메소드에 인가처리(권한심사) 기능을 하는 Advice를 등록
- 빈 참조시 실제 빈이 아닌 프록시 빈 객체를 참조
- 진행과정
- 메소드 호출 시 프록시 객체를 통해 메소드를 호출
- Advice가 등록되어 있다면 Advice를 작동하게 하여 인가 처리
- 권한 심사 통과하면 실제 빈의 메소드를 호출한다.
- 초기화 과정
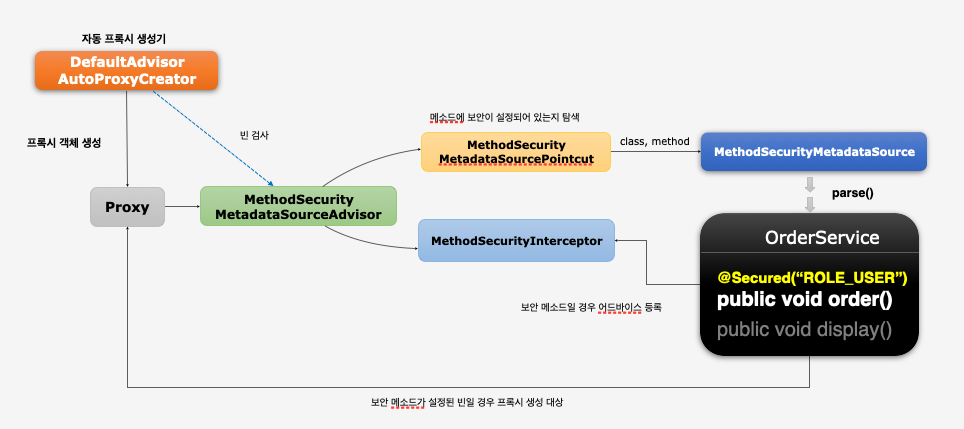
- 정리하면 다음과 같다. 스프링은 Advisor를 등록하고 컨테이너에 등록되는 빈을 pointcut를 이용하여 검사한다. pointcut에 해당되면 프록시 객체를 생성하고 프록시를 빈으로 등록하게 된다.
MethodSecurityMetadataSourcePointcut은method와targetClass의 정보를 이용하여 애노테이션이 붙었는지 여부를 검사함으로써 매칭 여부를 검사한다. 매칭이 되면 Advice(MethodSecurityInterceptor)를 적용한 프록시 객체를 생성하고 빈으로 등록한다. 프록시 참조가 호출되면 먼저 Advice가 적용된 메소드인지 판단한다. 적용되어 있다면 호출된 method 정보와 함께MethodSecurityInterceptor를 호출한다.MethodSecurityInterceptor에서는pointcut과 유사하게method와targetClass의 정보를 이용하여Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes를 가져오고 인가 로직을 태운다. 이후 예외가 발생하거나 그렇지 않다면 실체 호출된 메소드가 호출된다.
Map 기반 DB 연동 (1)
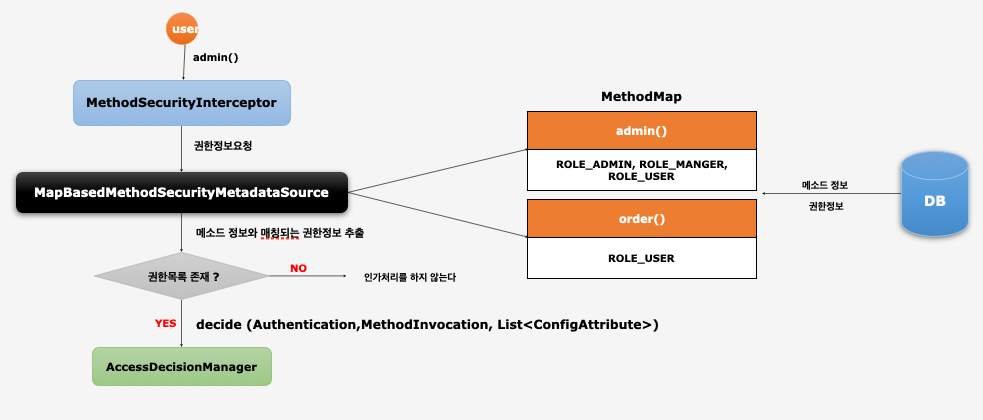
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
@Configuration
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
@Override
protected MethodSecurityMetadataSource customMethodSecurityMetadataSource() {
return new MapBasedMethodSecurityMetadataSource( );
}
}
### Map 기반 DB 연동 (2)
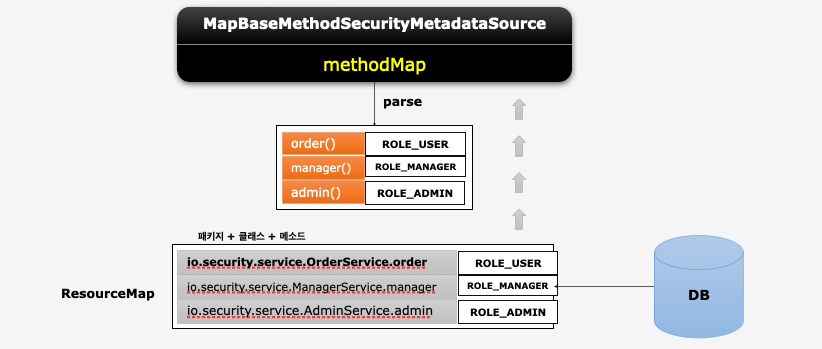
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
@Configuration
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
@Autowired
private SecurityResourceService securityResourceService;
@Override
protected MethodSecurityMetadataSource customMethodSecurityMetadataSource() {
return new MapBasedMethodSecurityMetadataSource(methodResourcesMapFactoryBean().getObject());
}
@Bean
public FactoryBean methodResourcesMapFactoryBean() {
MethodResourcesFactoryBean methodResourcesFactoryBean = new MethodResourcesFactoryBean();
methodResourcesFactoryBean.setSecurityResourceService(securityResourceService);
return methodResourcesFactoryBean;
}
}
public class MethodResourcesFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<LinkedHashMap<String, List<ConfigAttribute>>> {
private SecurityResourceService securityResourceService;
private LinkedHashMap<String, List<ConfigAttribute>> resourceMap;
public void setSecurityResourceService(SecurityResourceService securityResourceService) {
this.securityResourceService = securityResourceService;
}
@Override
public LinkedHashMap<String, List<ConfigAttribute>> getObject() { // String: Package + Class + Method
if (resourceMap == null) {
init();
}
return resourceMap;
}
private void init() {
resourceMap = securityResourceService.getResourceList();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return LinkedHashMap.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
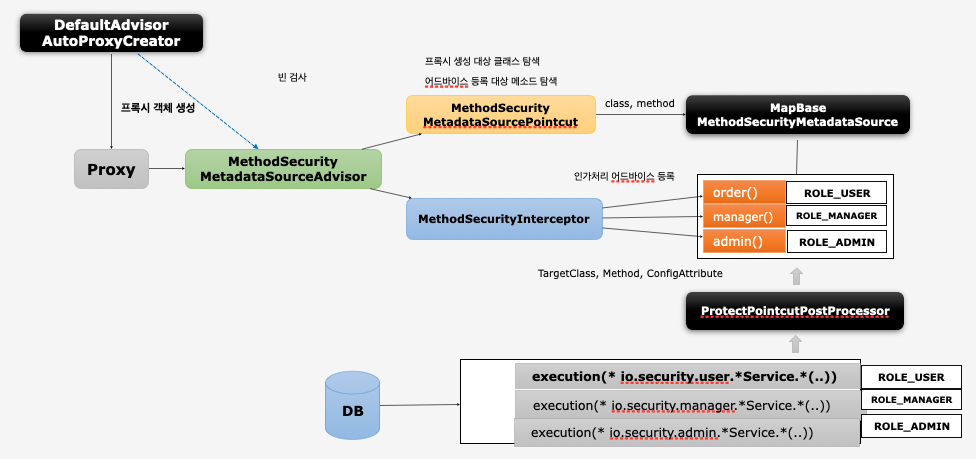
ProtectPointcutPostProcessor
- 메소드 방식의 인가처리를 위한 자원 및 권한정보 설정시 자원에 포인트 컷 표현식을 사용할 수 있도록 지원하는 클래스
- 빈 후처리기로서 스프링 초기화 과정에서 빈 들을 검사하여 빈이 가진 메소드 중에서 포인트 컷 표현식과 matching 되는 클래스, 메소드, 권한 정보를
MapBasedMethodSecurityMetadataSource에 전달하여 인가처리가 되도록 제공되는 클래스 - 설정 클래스에서 빈 생성시 접근제한자가 package 범위로 되어 있기 때문에 직접
ProtectPointcutPostProcessor을 만들어서 빈으로 등록해야 한다.attemptMatch메소드는try~catch문으로 감싸야 에러처리가 가능해진다. ProtectPointcutPostProcessor는BeanPostProcessor를 구현하고 있는데postProcessBeforeInitialization메소드 안에서attemptMatch를 호출한다.attemptMatch는 포인트컷 매칭여부를 검사하고 메소드가 포인트컷에 매칭이 되면Map<String, List<ConfigAttribute>> pointcutMap에서(String: 포인트컷) 권한 정보를 가져와서MapBasedMethodSecurityMetadataSource로 넘긴다. 그러면MapBasedMethodSecurityMetadataSource에서Map<RegisteredMethod, List<ConfigAttribute>> methodMap에 저장을 한다. 이렇게 되면 프록시 팩토리에서 Advisor의 포인트컷으로 매칭여부를 검사하고 해당되면 Advice를 적용하고 프록시 객체를 생성한 후 빈으로 등록한다.

댓글남기기